Write: Daml Studio¶
Daml Studio is an integrated development environment (IDE) for Daml. It is an extension on top of Visual Studio Code (VS Code), a cross-platform, open-source editor providing a rich code editing experience.
Install¶
Daml Studio is included in the Daml SDK.
Create Your First Daml File¶
Start Daml Studio by running
daml studioin the current project.This command starts Visual Studio Code and (if needs be) installs the Daml Studio extension, or upgrades it to the latest version.
Make sure the Daml Studio extension is installed:
- Click on the Extensions icon at the bottom of the VS Code sidebar.
- Click on the Daml Studio extension that should be listed on the pane.
Open a new file (
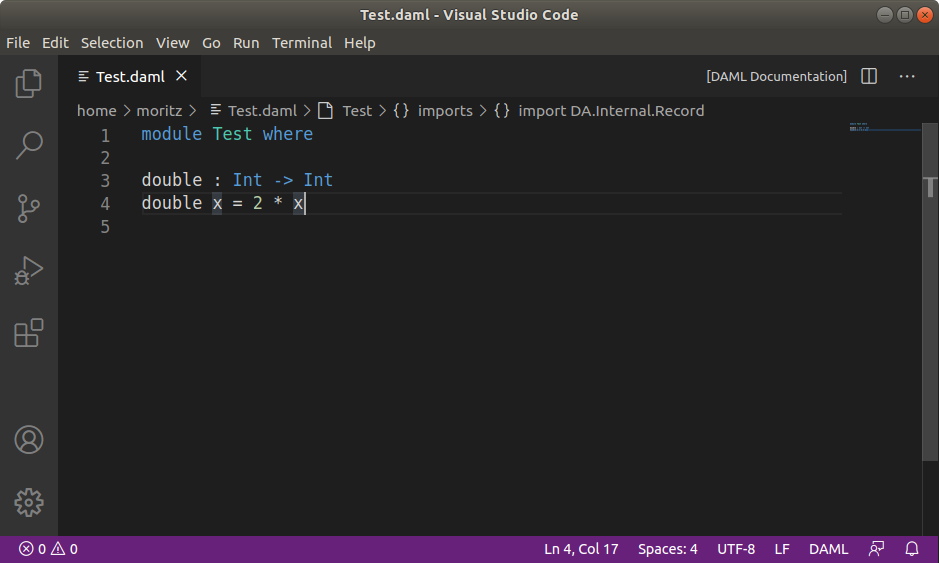
⌘N) and save it (⌘S) asTest.daml.Copy the following code into your file:
module Test where
double : Int -> Int
double x = 2 * x
Your screen should now look like the image below.
Introduce a parse error by deleting the
=sign and then clicking the Ⓧ symbol on the lower-left corner. Your screen should now look like the image below.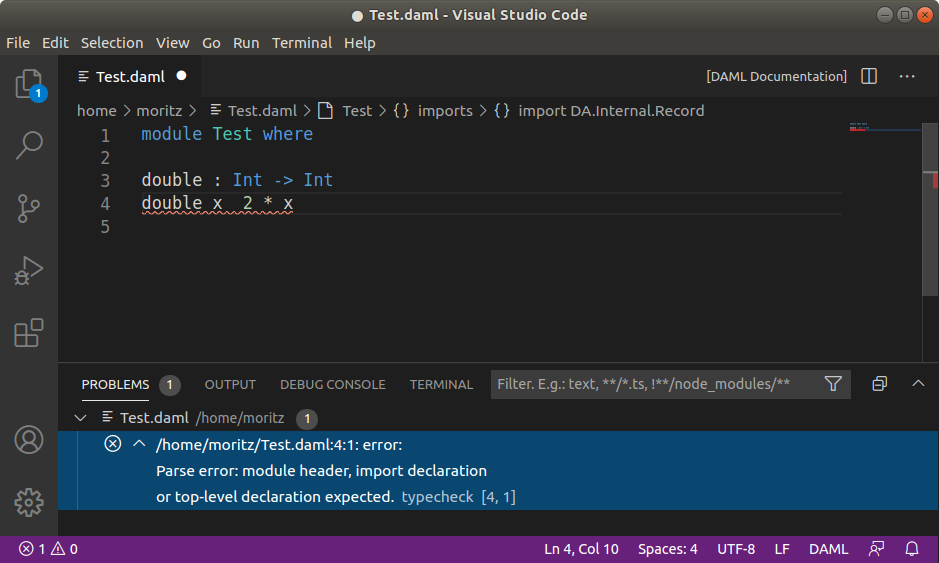
Remove the parse error by restoring the
=sign.
We recommend reviewing the Visual Studio Code documentation to learn more about how to use it. To learn more about Daml, see Language Reference.
Supported Features¶
Visual Studio Code provides many helpful features for editing Daml files and we recommend reviewing Visual Studio Code Basics and Visual Studio Code Keyboard Shortcuts for OS X. The Daml Studio extension for Visual Studio Code provides the following Daml-specific features:
Symbols and Problem Reporting¶
Use the commands listed below to navigate between symbols, rename them, and inspect any problems detected in your Daml files. Symbols are identifiers such as template names, lambda arguments, variables, and so on.
| Command | Shortcut (OS X) |
|---|---|
| Go to Definition | F12 |
| Peek Definition | ⌥F12 |
| Rename Symbol | F2 |
| Go to Symbol in File | ⇧⌘O |
| Go to Symbol in Workspace | ⌘T |
| Find all References | ⇧F12 |
| Problems Panel | ⇧⌘M |
Note
You can also start a command by typing its name into the command palette (press ⇧⌘P or F1). The command palette
is also handy for looking up keyboard shortcuts.
Note
- Rename Symbol, Go to Symbol in File, Go to Symbol in Workspace, and Find all References work on: choices, record fields, top-level definitions, let-bound variables, lambda arguments, and modules
- Go to Definition and Peek Definition work on: top-level definitions, let-bound variables, lambda arguments, and modules
Hover Tooltips¶
You can hover over most symbols in the code to display additional information such as its type.
Daml Script Results¶
Top-level declarations of type Script are decorated with
a Script results code lens.
You can click on the code lens to inspect the
execution transaction graph and the active contracts.
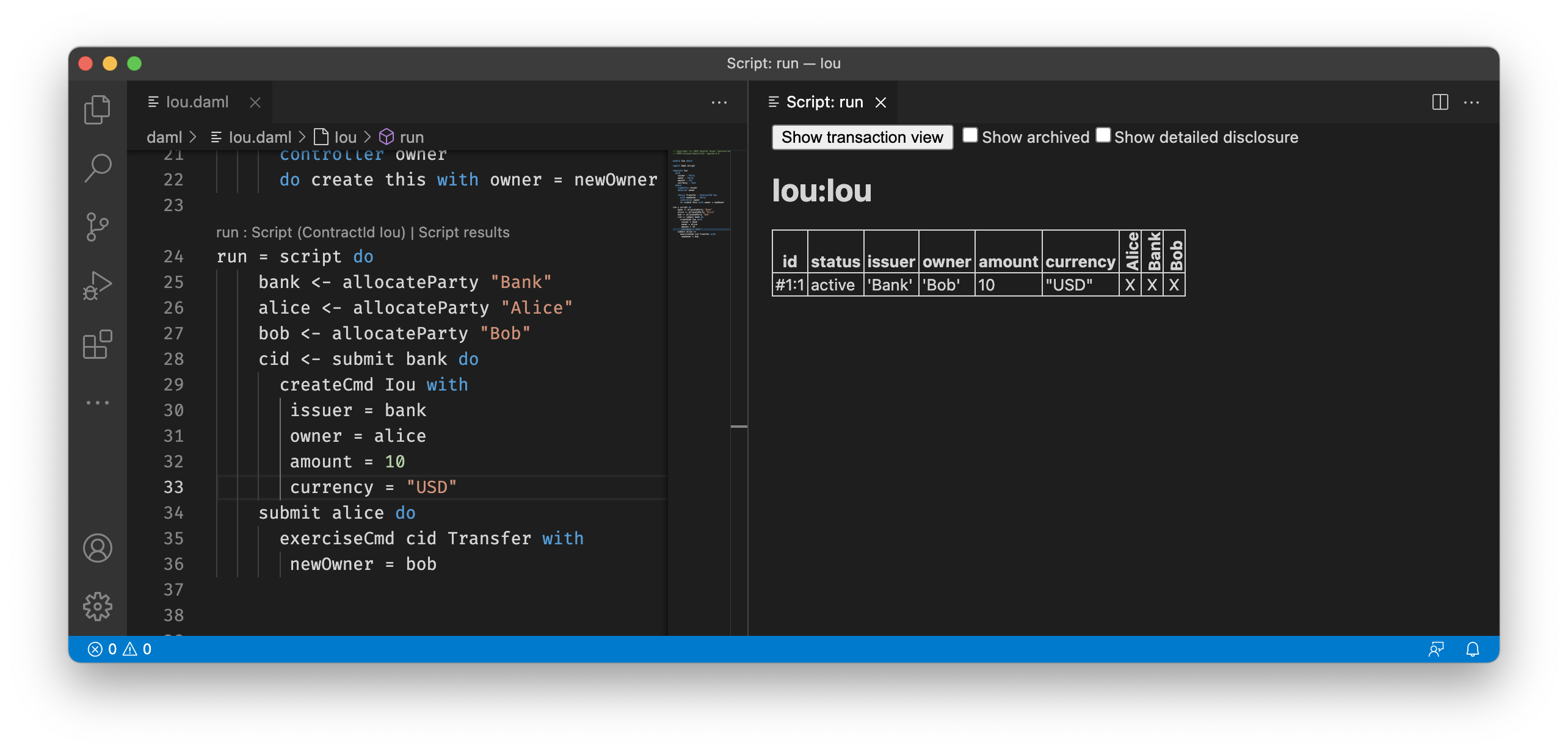
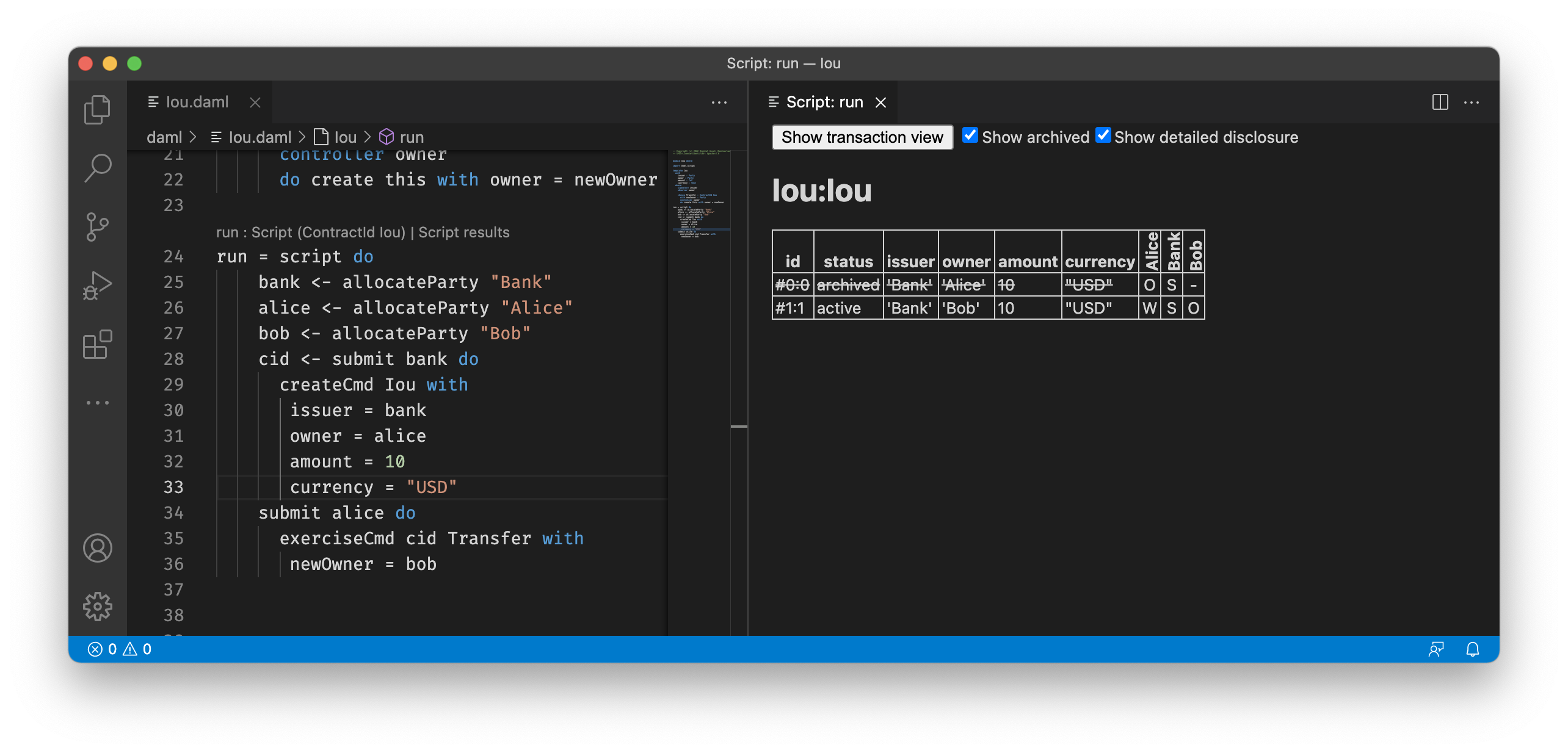
For the script from the Iou
module, you get the following table displaying all contracts that are
active at the end of the script. The first column displays the
contract id. The columns afterwards represent the fields of the
contract and finally you get one column per party with an X if the
party can see the contract or a - if not.
If you want more details, you can click on the Show archived checkbox, which extends the table to include archived contracts, and on the Show detailed disclosure checkbox, which displays why the contract is visible to each party, based on four categories:
S, the party sees the contract because they are a signatory on the contract.O, the party sees the contract because they are an observer on the contract.W, the party sees the contract because they witnessed the creation of this contract, e.g., because they are an actor on theexercisethat created it.D, the party sees the contract because they have been divulged the contract, e.g., because they witnessed an exercise that resulted in afetchof this contract.
For details on the meaning of those four categories, refer to the
Daml Ledger Model.
For the example above, the resulting table looks as follows. You can see the
archived Bank contract and the active Bank contract whose creation
Alice has witnessed by virtue of being an actor on the exercise that
created it.
If you want to see the detailed transaction graph you can click on the
Show transaction view button. The transaction graph
consists of transactions, each of which contain one or more updates to the
ledger, that is creates and exercises. The transaction graph also records
fetches of contracts.
For example a script for the Iou module looks as follows:
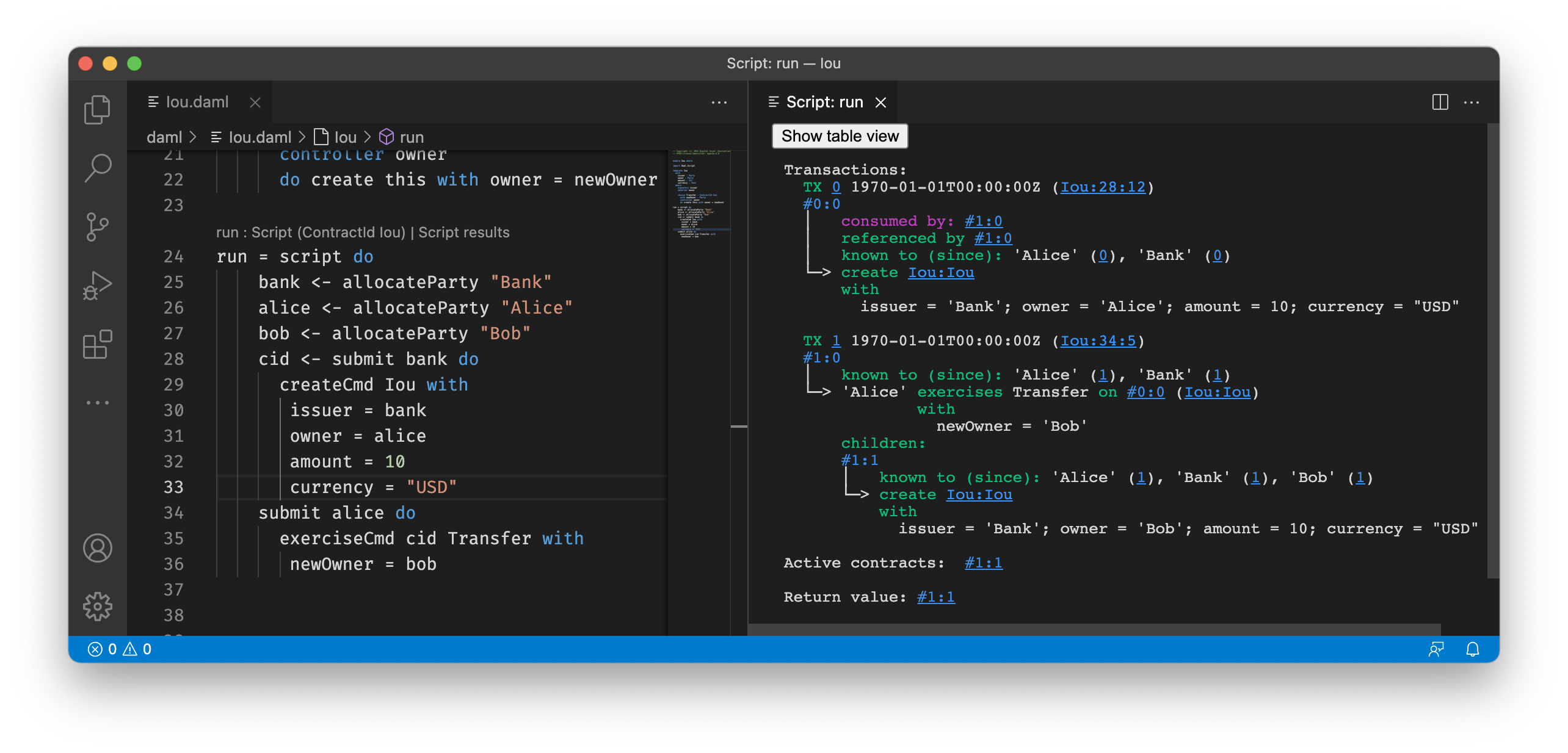
Script results¶
Each transaction is the result of executing a step in the script. In the
image below, the transaction #0 is the result of executing the first
line of the script (line 20), where the Iou is created by the bank. The following
information can be gathered from the transaction:
- The result of the first script transaction
#0was the creation of theIoucontract with the argumentsbank,10, and"USD". - The created contract is referenced in transaction
#1, step0. - The created contract was consumed in transaction
#1, step0. - A new contract was created in transaction
#1, step1, and has been divulged to parties ‘Alice’, ‘Bob’, and ‘Bank’. - At the end of the script only the contract created in
#1:1remains. - The return value from running the script is the contract identifier
#1:1. - And finally, the contract identifiers assigned in script execution correspond to
the script step that created them (e.g.
#1).
You can navigate to the corresponding source code by clicking on the location
shown in parenthesis (e.g. Iou:25:12, which means the Iou module, line 25 and column 1).
You can also navigate between transactions by clicking on the transaction and contract ids (e.g. #1:0).
Daml Snippets¶
You can automatically complete a number of “snippets” when editing a Daml
source file. By default, hitting ^-Space after typing a Daml keyword
displays available snippets that you can insert.
To define your own workflow around Daml snippets, adjust your user settings in Visual Studio Code to include the following options:
{
"editor.tabCompletion": true,
"editor.quickSuggestions": false
}
With those changes in place, you can simply hit Tab after a keyword to insert the code pattern.
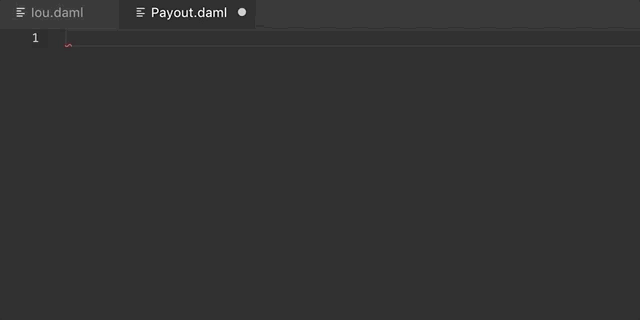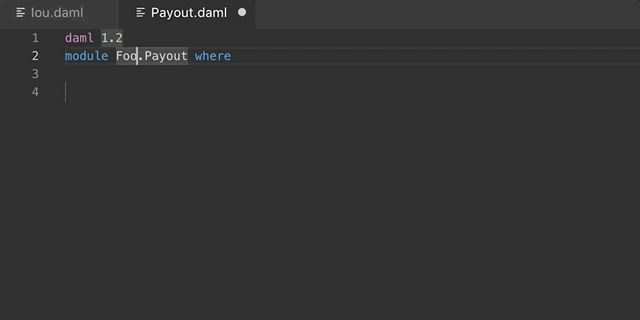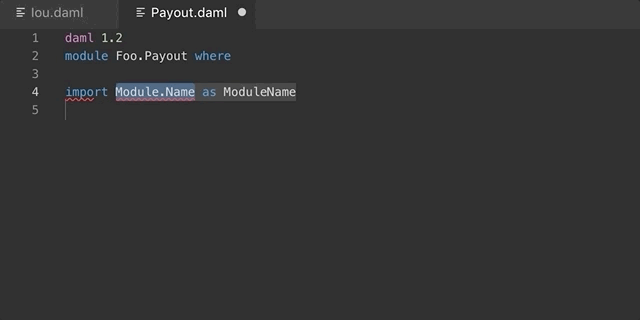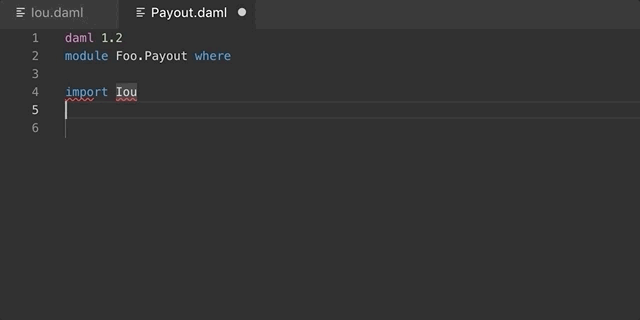
You can develop your own snippets by following the instructions in
Creating your own Snippets to create an appropriate daml.json
snippet file.
Common Script Errors¶
During Daml execution, errors can occur due to exceptions (e.g. use of “abort”, or division by zero), or due to authorization failures. You can expect to run into the following errors when writing Daml.
When a runtime error occurs in a script execution, the script result view shows the error together with the following additional information, if available:
- Location of the failed commit
- If the failing part of the script was a
submitCmd, the source location of the call tosubmitCmdwill be displayed. - Stack trace
- A list of source locations that were encountered before the error occurred. The last encountered location is the first entry in the list.
- Ledger time
- The ledger time at which the error occurred.
- Partial transaction
- The transaction that is being constructed, but not yet committed to the ledger.
- Committed transaction
- Transactions that were successfully committed to the ledger prior to the error.
- Trace
- Any messages produced by calls to
traceanddebug.
Abort, Assert, and Debug¶
The abort, assert and debug inbuilt functions can be used in updates and scripts. All three can be used to output messages, but abort and assert can additionally halt the execution:
abortTest = script do
debug "hello, world!"
abort "stop"
Script execution failed:
Unhandled exception: DA.Exception.GeneralError:GeneralError with
message = "stop"
Ledger time: 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z
Trace:
"hello, world!"
Missing Authorization on Create¶
If a contract is being created without approval from all authorizing parties the commit will fail. For example:
template Example
with
party1 : Party; party2 : Party
where
signatory party1
signatory party2
example = script do
alice <- allocateParty "Alice"
bob <- allocateParty "Bob"
alice `submit` createCmd Example with
party1 = alice
party2 = bob
Execution of the example script fails due to ‘Bob’ being a signatory in the contract, but not authorizing the create:
Script execution failed:
#0: create of CreateAuthFailure:Example at unknown source
failed due to a missing authorization from 'Bob'
Ledger time: 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z
Partial transaction:
Sub-transactions:
#0
└─> Alice creates CreateAuthFailure:Example
with
party1 = 'Alice'; party2 = 'Bob'
To create the “Example” contract one would need to bring both parties to authorize the creation via a choice, for example ‘Alice’ could create a contract giving ‘Bob’ the choice to create the ‘Example’ contract.
Missing Authorization on Exercise¶
Similarly to creates, exercises can also fail due to missing authorizations when a party that is not a controller of a choice exercises it.
template Example
with
owner : Party
friend : Party
where
signatory owner
observer friend
choice Consume : ()
controller owner
do return ()
choice Hello : ()
controller friend
do return ()
example = script do
alice <- allocateParty "Alice"
bob <- allocateParty "Bob"
cid <- alice `submit` createCmd Example with
owner = alice
friend = bob
bob `submit` exerciseCmd cid Consume
The execution of the example script fails when ‘Bob’ tries to exercise the choice ‘Consume’ of which he is not a controller
Script execution failed:
#1: exercise of Consume in ExerciseAuthFailure:Example at unknown source
failed due to a missing authorization from 'Alice'
Ledger time: 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z
Partial transaction:
Failed exercise:
exercises Consume on #0:0 (ExerciseAuthFailure:Example)
with
Sub-transactions:
0
└─> 'Alice' exercises Consume on #0:0 (ExerciseAuthFailure:Example)
with
Committed transactions:
TX #0 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z (unknown source)
#0:0
│ disclosed to (since): 'Alice' (#0), 'Bob' (#0)
└─> 'Alice' creates ExerciseAuthFailure:Example
with
owner = 'Alice'; friend = 'Bob'
From the error we can see that the parties authorizing the exercise (‘Bob’) is not a subset of the required controlling parties.
Contract Not Visible¶
Contract not being visible is another common error that can occur when a contract that is being fetched or exercised has not been disclosed to the committing party. For example:
template Example
with owner: Party
where
signatory owner
choice Consume : ()
controller owner
do return ()
example = script do
alice <- allocateParty "Alice"
bob <- allocateParty "Bob"
cid <- alice `submit` createCmd Example with owner = alice
bob `submit` exerciseCmd cid Consume
In the above script the ‘Example’ contract is created by ‘Alice’ and makes no mention of the party ‘Bob’ and hence does not cause the contract to be disclosed to ‘Bob’. When ‘Bob’ tries to exercise the contract the following error would occur:
Script execution failed:
Attempt to fetch or exercise a contract not visible to the reading parties.
Contract: #0:0 (NotVisibleFailure:Example)
actAs: 'Bob'
readAs:
Disclosed to: 'Alice'
Ledger time: 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z
Partial transaction:
Committed transactions:
TX #0 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z (unknown source)
#0:0
│ disclosed to (since): 'Alice' (#0)
└─> 'Alice' creates NotVisibleFailure:Example
with
owner = 'Alice'
To fix this issue the party ‘Bob’ should be made a controlling party in one of the choices.
Multi-Package Support¶
Following the Multi-Package support added to daml build (see here),
Daml Studio also supports projects that utilize the multi-package.yaml file.
You should become familiar with multi-package builds
before continuing in this section.
The Daml Studio Multi-IDE feature runs separate package environments for
each package in your project, and allows cross-package jump-to-definition for
any packages listed in a top level multi-package.yaml file.
Multi-package.yaml Location¶
Daml Studio only uses the multi-package.yaml file if it sits at the
VS Code Workspace Root, that is, in the root directory in which Daml Studio was opened.
If no multi-package.yaml is found, the cross-package jump-to-definition feature
cannot jump to the real on-disk source code, however, other Multi-IDE features still work as normal.
Package Environments and Hot-Loading¶
The Multi-IDE runs a separate package environment for each package in the project,
allowing the IDE to replicate properties such as dependencies, module-prefixes, and build-options
of each package individually, without clashing with other packages in the project.
A package’s environment automatically reloads if its daml.yaml file changes,
or any of the dependency DAR files change.
Note, however, that the Multi-IDE does not hold “live” copies of DARs, therefore any changes
to a package that is a dependency of another package are not visible in that second package until
you run daml build.
You can run daml build --all to rebuild all relevant DARs. The IDE accounts for this
and reloads environments as necessary.
Jumping to definition on non-local dependencies (those not listed in multi-package.yaml)
also uses the correct environment, giving correct diagnostics for that package, and allowing
further jumps down the stack. However, this can only jump to a package for which the source code is available, that is packages to which the DAR can be found in any of the following places:
- The data-dependencies field of the current package or any other packages known to the multi-package.yaml
- Under the added dars field in the multi-package.yaml, which is shown below:
packages:
- my-package
- libs/my-lib
dars:
# Given my-package depends on some DAR, which then depends on my-transitive-dependency
- ./dars/my-transitive-dependency-1.0.0.dar
Adding DAR paths to this field has no effect on building, serving only for the IDE to jump to.
Multiple Daml SDK Versions¶
Separate package environments can run in different Daml SDK versions (though some features may not work correctly in versions <= 2.8). When opening a file, or jumping to a location in a package running a Daml version that is not currently installed, Daml Studio prompts you to install the missing Daml SDK, and then handles the installation, progress reporting, and cancellation within a notification.
Directory Envrionment Tools (direnv)¶
Tools like direnv are commonly used to set up dependencies and import environment variables
for use with environment variable interpolation support. To make this work in Daml Studio,
you need a VSCode extension that sets this up for other extensions.
In the case of direnv specifically (i.e. you have a .envrc file), we
recommend using this direnv extension by Martin Kühl, which we have verified is compatible.
Other direnv extensions may not correctly pass environment information to the Daml Studio extension.
If the Daml extension detects a .envrc file, it recommends this extension within the IDE with the
following message:
..code:
Found an .envrc file but the recommended direnv VSCode extension is not installed. Daml IDE may fail to start due to missing environment variables.
Would you like to install the recommended direnv extension or attempt to continue without it?
It also provides a link to the extension on the VS Code extension marketplace.
Limitations in 2.10.0-rc¶
These limitations are for the Release Candidate only, not for the 2.10 full release.
- Jumping to non-local dependencies does not currently retain the build-options and module-prefixes for that package. This means that if you jump to a dependency that requires either of these to build, the editor shows errors in the source code.
- Some links in the Script Results tab may not resolve correctly cross-package.
- Packages with symlinks between the daml.yaml and source files may not give correct intelligence.
Setting Multi-IDE SDK Version¶
The Multi-IDE selects the correct SDK version for each package you interact with. However the
Multi-IDE itself runs from your most recently installed SDK version. You can override this using
an additional daml.yaml file at the root of your project (next to the multi-package.yaml)
containing only an SDK Version, as follows:
.
├── daml.yaml
├── multi-package.yaml
├── pkga
│ ├── daml
│ │ └── A.daml
│ └── daml.yaml
└── pkgb
├── daml
│ └── B.daml
└── daml.yaml
The root daml.yaml contains only the sdk-version field, as shown below.
Note that Multi-IDE is only supported in 2.10+.
sdk-version: 2.10.0
This feature can also be used when Multi-IDE is inactive, as described below.