Building Applications¶
This page describes the patterns to follow when building applications using Daml Finance.
Installing Daml Finance¶
Each Daml SDK release defines a set of consistent Daml Finance package versions that have been
tested to work with each other. The list of package versions for each Daml SDK release can be found
here. To facilitate getting started with a particular release set, the Daml SDK
comes with a quickstart-finance template that contains a script to download these packages.
After installing the Daml SDK, you can execute the following commands to create a new Daml Finance project based on the set of packages released with the given SDK version:
On Unix-based systems execute:
daml new quickstart-finance --template=quickstart-finance
cd quickstart-finance
./get-dependencies.sh
On Windows-based systems execute:
daml new quickstart-finance --template=quickstart-finance
cd quickstart-finance
get-dependencies.bat
You can then edit the daml.yaml file and uncomment the lines corresponding to the packages you
require in your project.
Alternatively, if you want to install the latest Daml Finance version into an existing project, you can copy and execute these scripts (Unix and Windows variants) from the main branch of the repository.
Application Architecture¶
When building applications using Daml Finance it is important to ensure your application only depends on the interface layer (i.e., the public API) of Daml Finance. Furthermore, it is suggested that your application follows a similar split between interface (API) and implementation layer in order to maximize upgradability and minimize the impact of incremental changes to your application or Daml Finance.
The following picture shows a suggested architecture that minimizes undesirable coupling and optimizes for upgradability of your application:
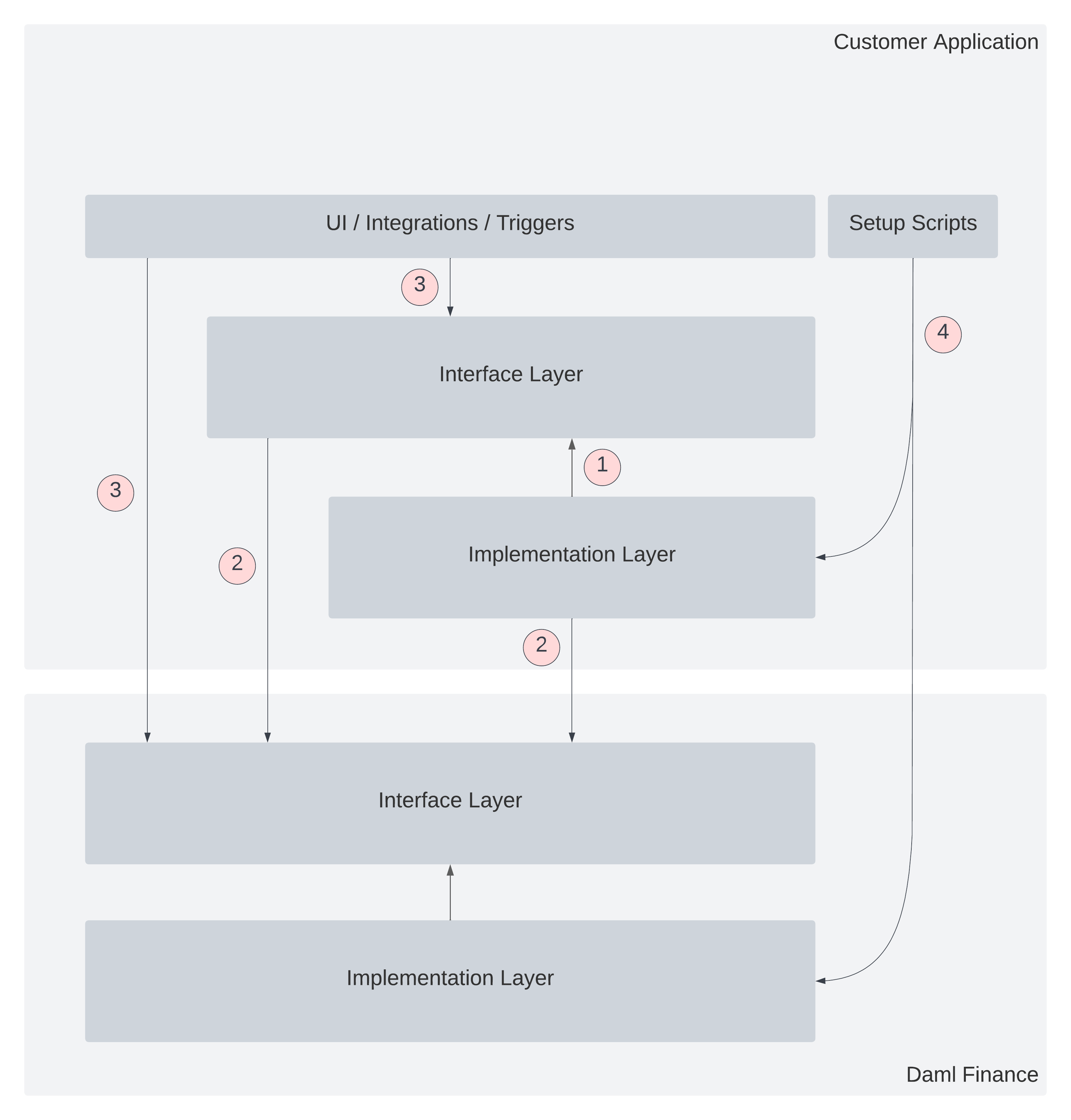
The following annotations are highlighted in the diagram:
- The customer application should be split into an implementation and an interface (API) layer. This ensures that implementations can be upgraded without affecting client-side applications, like the UI, integrations, or Daml Triggers (deprecated).
- The customer application (both the interface and implementation layer) should only depend on the interface layer (API) of Daml Finance. This ensures that upgrades to the implementation layer of Daml Finance do not affect the Customer Application.
- All client-side code (UI, integrations, Daml Triggers, etc.) should only depend on the interface layers of Daml Finance and the Customer Application. This ensures that any implementation upgrades in Daml Finance or the Customer Application do not affect client-side code.
- Any setup scripts used to initialize the application can (and usually have to) depend on the implementation layers of Daml Finance and the Customer Application. This is required to set up contracts like factories, where a dependency on the implementation package is needed. It does not affect the overall upgradability of the Customer Application as these operations are usually executed either at initial setup or on a one-off basis, but not during normal operation of the application.
Following the above patterns ensures minimal impact of changes to any implementation part of the overall application:
- If a Daml Finance implementation package is upgraded, only the contracts for templates within the package have to be upgraded. The Customer Application itself is unaffected because it only depends on the interface packages, which remain unchanged.
- If a customer application implementation package is upgraded, only the contracts for templates within that package need to be upgraded. The client-side code of the application is unaffected, as it only depends on the Customer Application interface layer.
- If a Daml Finance interface package is upgraded, the affected parts in the customer application implementation, interface, or client-side layer need to be upgraded. To minimize the impact of such change it is suggested that the customer application layers themselves are divided into packages, that each depend on a minimal set of Daml Finance interface packages.
- If a customer application interface package is upgraded the corresponding implementation packages, as well as the affected client-side code have to be upgraded. Again, splitting up the interface (API) layer of the customer application can minimize the impact of such a change.
In general, we will provide upgrade contracts and scripts to facilitate migration between major version updates of packages within the Daml Finance perimeter.
Using Daml Codegen¶
The Daml Finance packages are compatible with the Daml Codegen tool.
If you, e.g., want to create a JavaScript app that uses Daml Finance, it is possible to generate JavaScript classes from the Daml Finance packages you need. Use daml codegen js, for example:
daml codegen js -o ./output .lib/daml-finance-interface-instrument-swap-0.2.1.dar .lib/daml-finance-interface-instrument-bond-0.2.1.dar
Alternatively, if your app uses Java, you can run daml codegen java in a similar way:
daml codegen java -o ./output .lib/daml-finance-interface-instrument-swap-0.2.1.dar .lib/daml-finance-interface-instrument-bond-0.2.1.dar
Note, this Daml Finance codegen is only supported on SDK versions 2.5.x and higher.

